A google indexing issue usually appears when Google cannot crawl or evaluate a page properly.
Even with great content, your pages may fail to appear on Google due to an underlying indexing issue.
Don’t panic if your page isn’t showing up on Google. This is a common issue and, in most cases, it’s surprisingly simple to fix once you identify the cause.
Here I’m Usama, SEO Specialist at SEO Service Care. Over the past 1.5 years, I’ve assisted multiple clients in resolving indexing issues through Google Search Console and technical SEO audits.
This guide, based on Google’s official recommendations, expert advice from John Mueller (Search Advocate at Google), and proven SEO practices. I’ll walk you through how to identify and fix googl indexing issue step-by-step. No shortcuts or black-hat methods.
SECTION 01
How Google Crawls, Indexes, and Ranks Pages
Before addressing google indexing issues, it’s important to know Google’s three-step process:
Crawling: Google’s bots explore your website by following links from page to page, discovering all available content.
Indexing: Once crawled, Google evaluates which pages are valuable and relevant, then stores this content in its database.
Ranking: Finally, Google decides which indexed pages to display in search results for specific queries, determining their order based on relevance and quality.
“Google doesn’t guarantee that it will crawl, index, or serve your page, even if your page follows the Google Search Essentials.”
[Source: developers.google.com]
In short, If Google doesn’t index a page, it won’t appear in search results. No matter how well you optimize it.
SECTION 02
How to Identify the Reasons for Google Indexing Issue
Before you fix a indexing problem, you need to know why Google is not indexing the page. Google Search Console can help you find out what is happening and why your page is missing from Google’s index.
[If you already know how to identify Google indexing issues, skip to Section 3 below.]
Check the Full Indexing Coverage Details
First, verify your website in Google Search Console (GSC) .
When you open Search Console, you’ll first see the Overview section on the main dashboard. Scroll down a little and you’ll see an interface like the one below. It shows how many pages are indexed and how many are not. To view the detailed breakdown, simply click on Full Report.
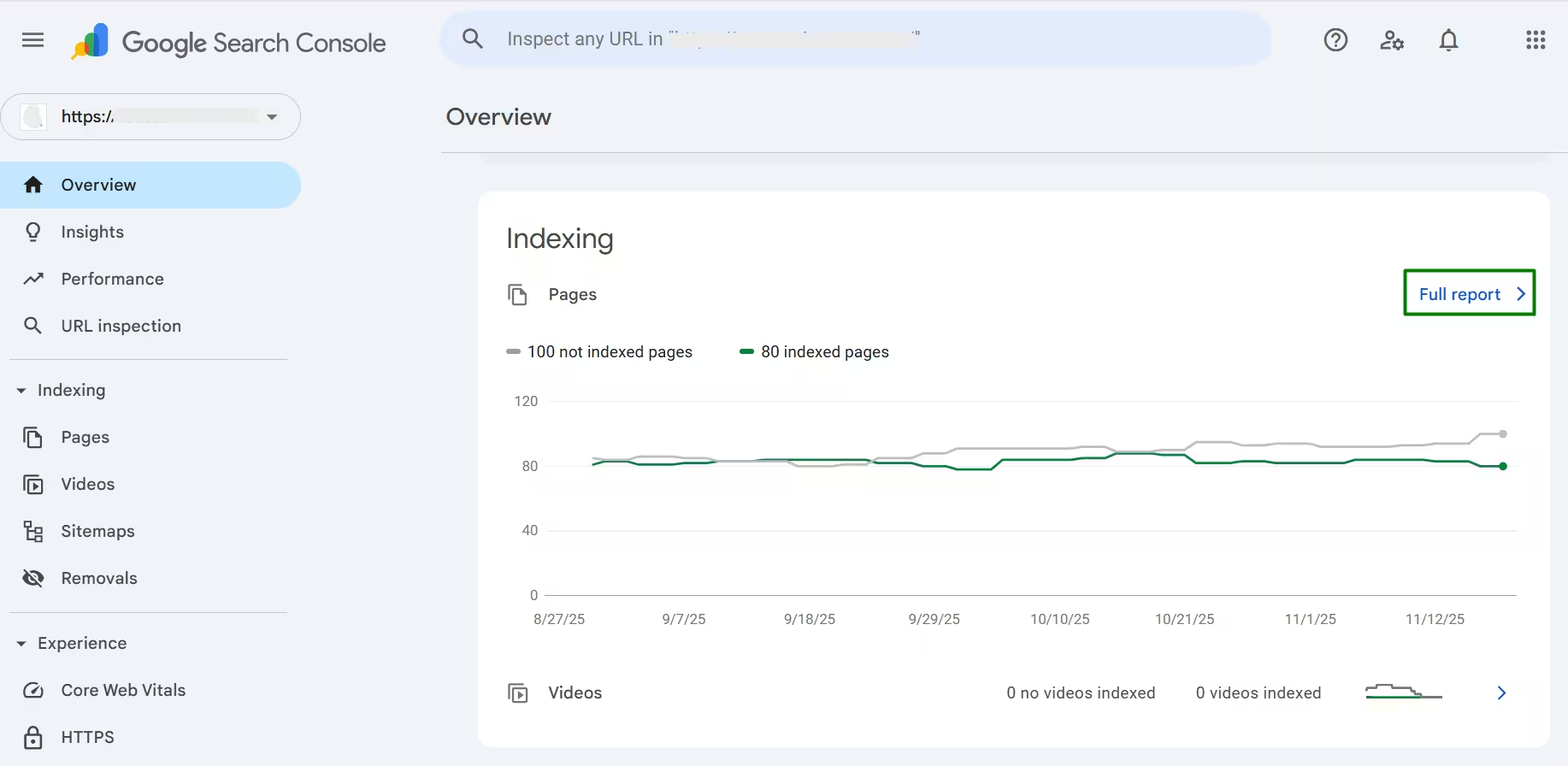
You can also open the full indexing report by going to Indexing in the dashboard and selecting Pages.
There you will see which pages are not indexed and the reasons behind it. There could be multiple reasons for this issue, including:
-
Not found (404)
-
Page with redirect
-
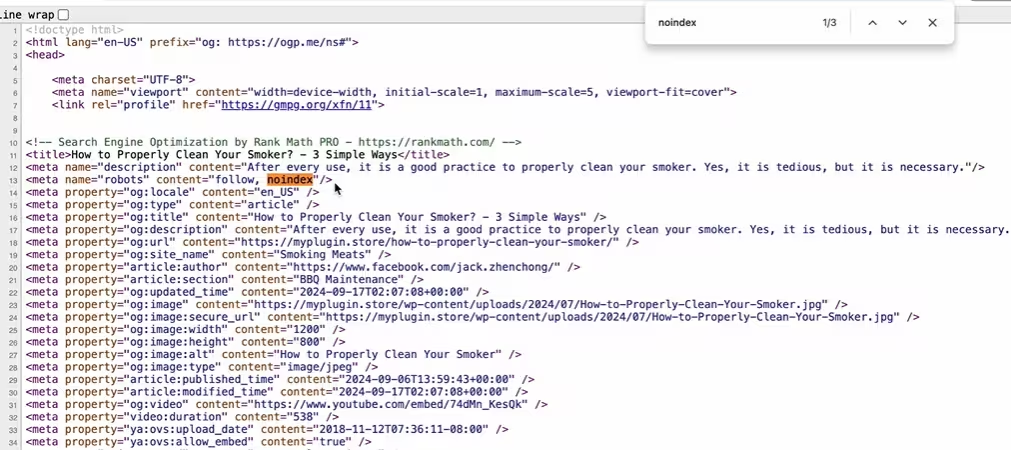
Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
-
Alternate page with proper canonical tag
-
Crawled – currently not indexed
-
Discovered – currently not indexed & etc.
I’m showing you the live Page Indexing coverage report from one of my ongoing projects, so you can see exactly which issues you might discover there.
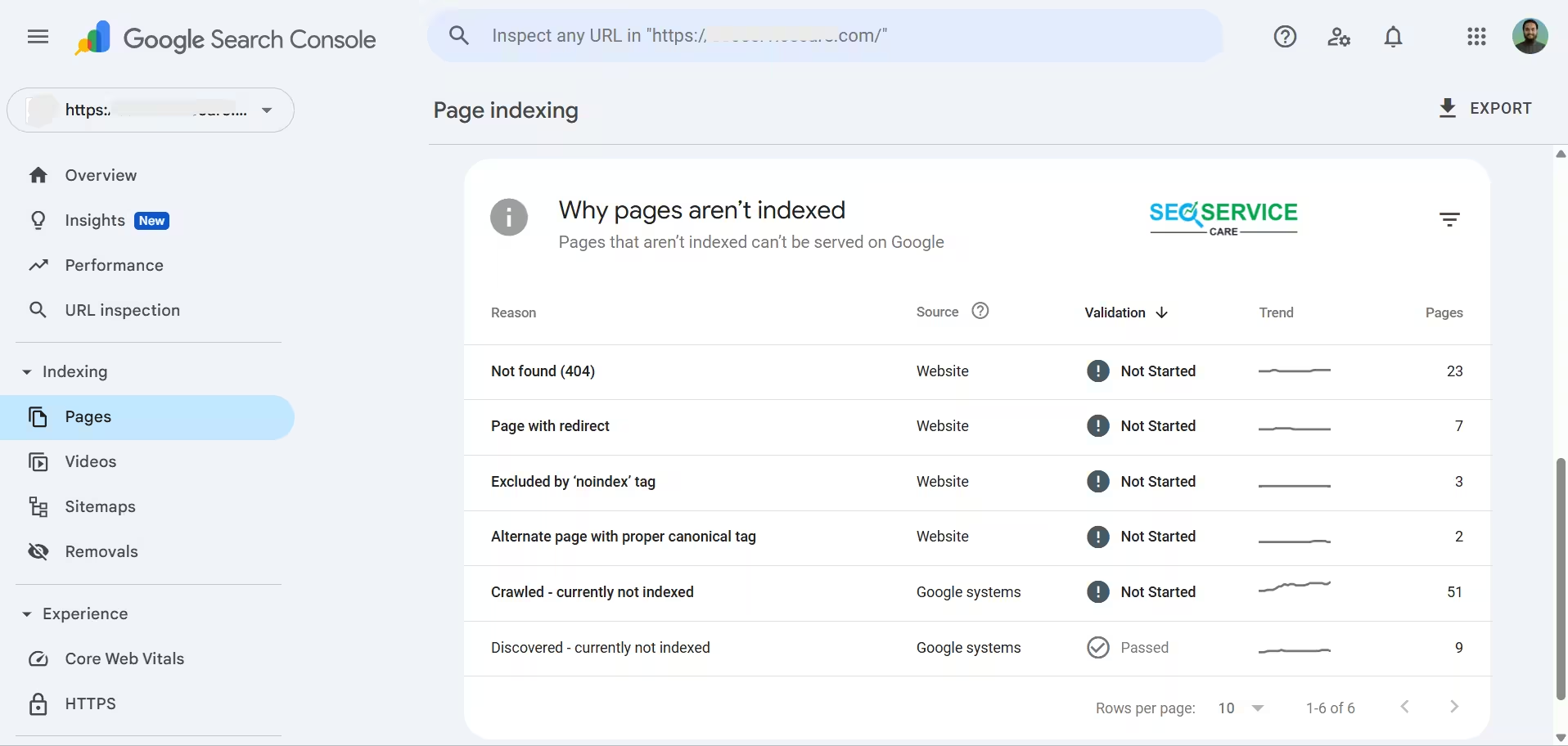
[Note: Website URLs and personal details have been blurred or removed to ensure confidentiality.]
Inspect a Specific URL
Use the URL Inspection Tool to specifically check a page.
In this section, you can use the search icon at the top of GSC and the Inspect URL option. Just enter your page URL to see its detailed status. As shown in the image below, you can see whether Google has indexed the page, when it last crawled it, and whether any noindex tags or canonical issues exist.
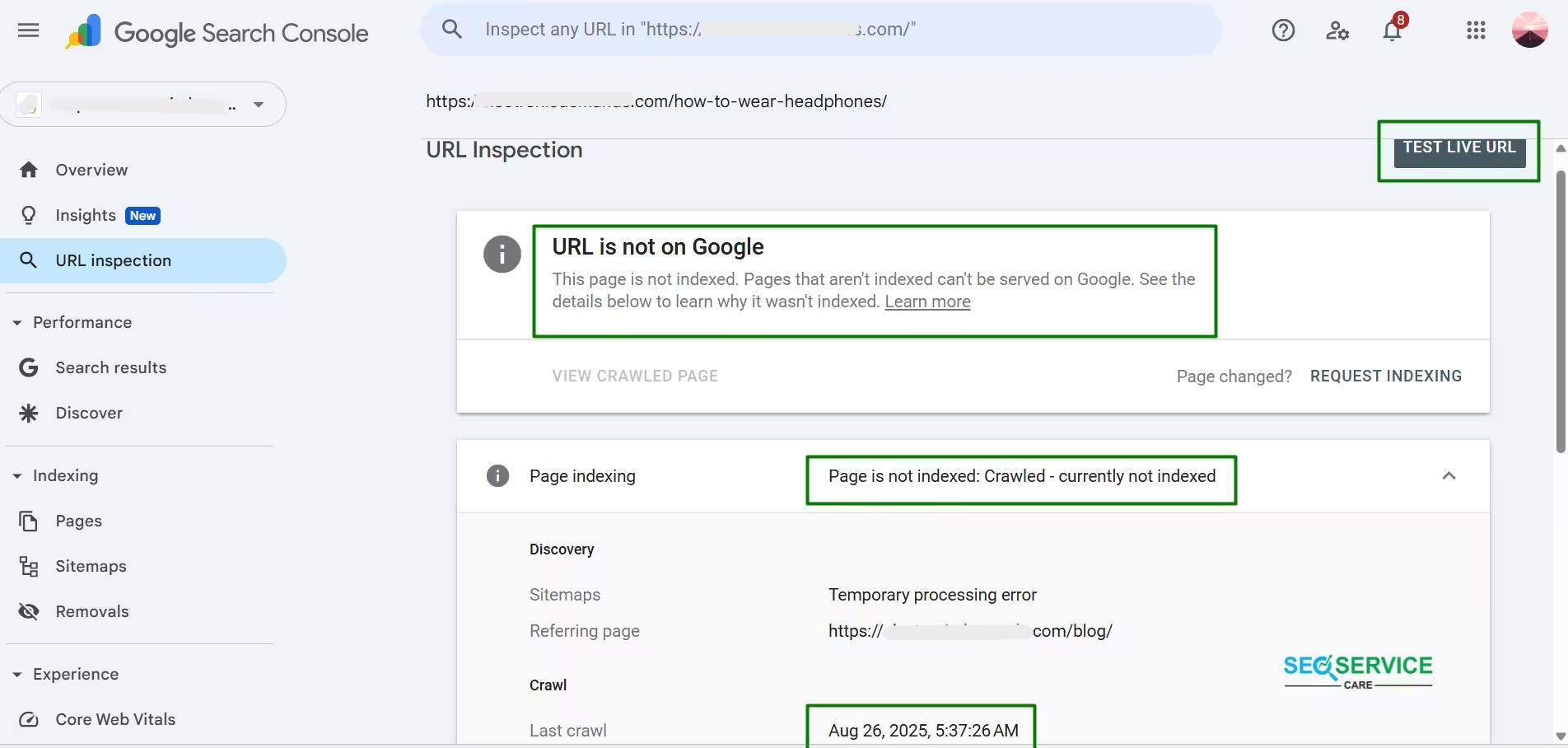
[The URL Inspection tool shows that Google has crawled the page but has not yet indexed it. The status displayed is “Crawled – currently not indexed.”]
Sometimes, pages are blocked by robots.txt, meta tags, or access errors, and this tool will show those issues clearly.
Use the ‘Test Live URL’ Option
To verify how Google is currently viewing your page in detail, click the Test Live URL button.
Steps:
URL Inspection → Test Live URL
Check the following:
• Can Google access the page without issues?
• Is it blocked by robots.txt or a noindex tag?
• Is the canonical URL set correctly?
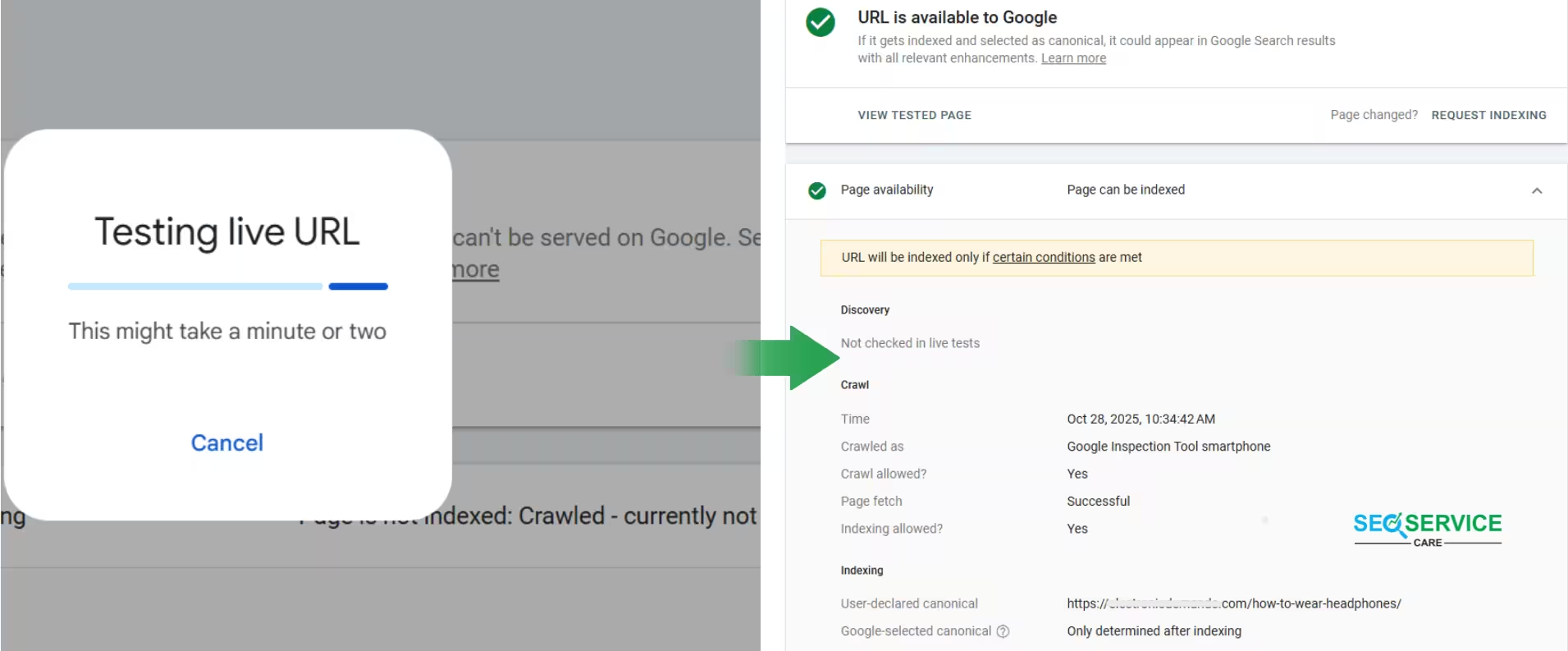
The report indicates that Google can access the page and there are no technical issues. In other words, there are no robots.txt blocks, noindex tags, or server errors. Google successfully crawled the page and was able to read its content. However, it has not yet been added to the search results.
The report also shows when Google last crawled the page and how it did so. The canonical URL for this page is set as https://main-domain/how-to-wear-headphones/. Google will decide during the indexing process whether to keep this URL as the canonical version or not.
Overall, the page is eligible for indexing, but Google has not yet added it to its index. This usually happens when you publish new content, your website has a lower crawl priority, or Google does not yet consider the content significant enough to index.
Compare with ‘site:’ Search
Open Google Search and enter site:yourdomain.com/page-url in the search bar.
If your page does not appear in the search results, it indicates that Google has not indexed the page yet.
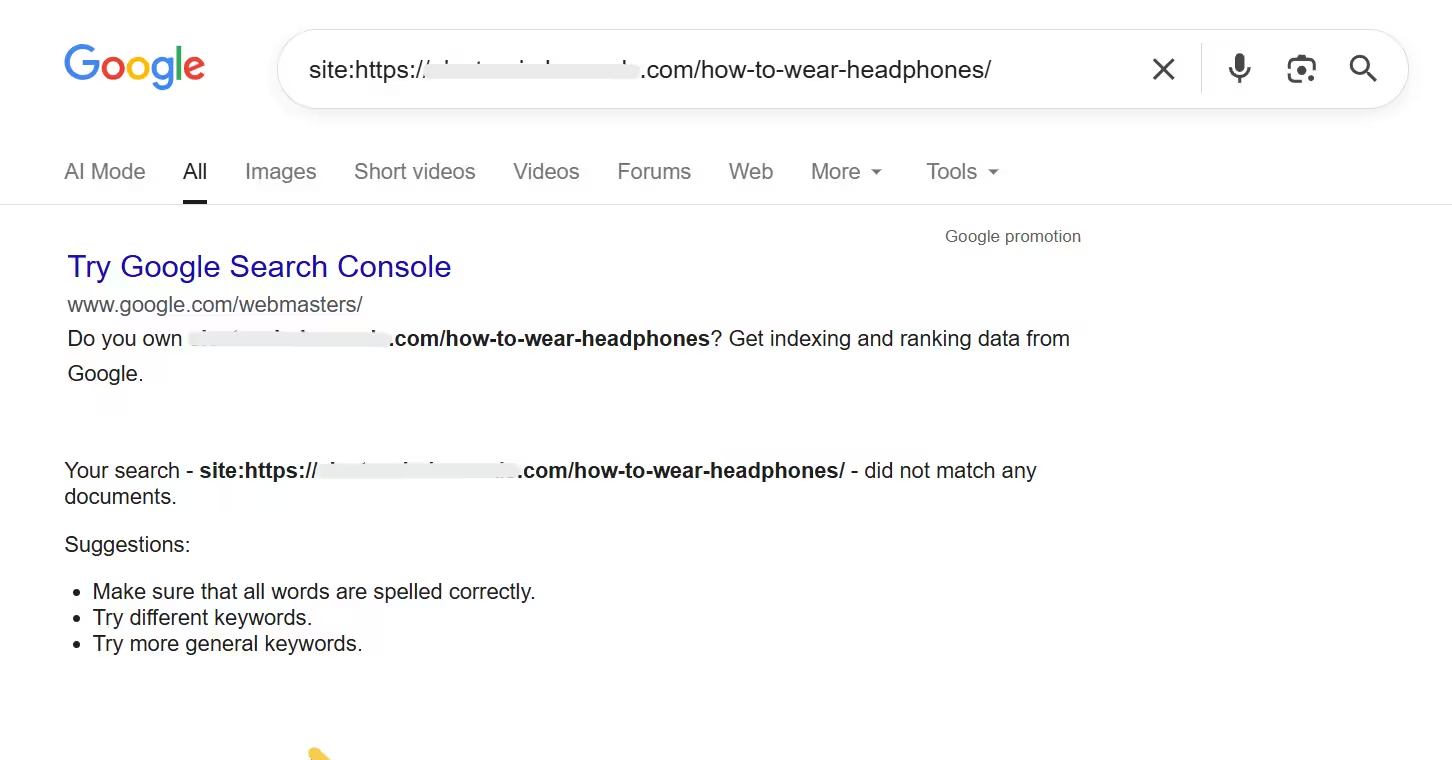
Comment: The URL displayed in the image is not yet indexed in Google.
Additionally, by using tools such as Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or Semrush, you can gain deeper insights into which pages are being crawled by Google but are not yet indexed.
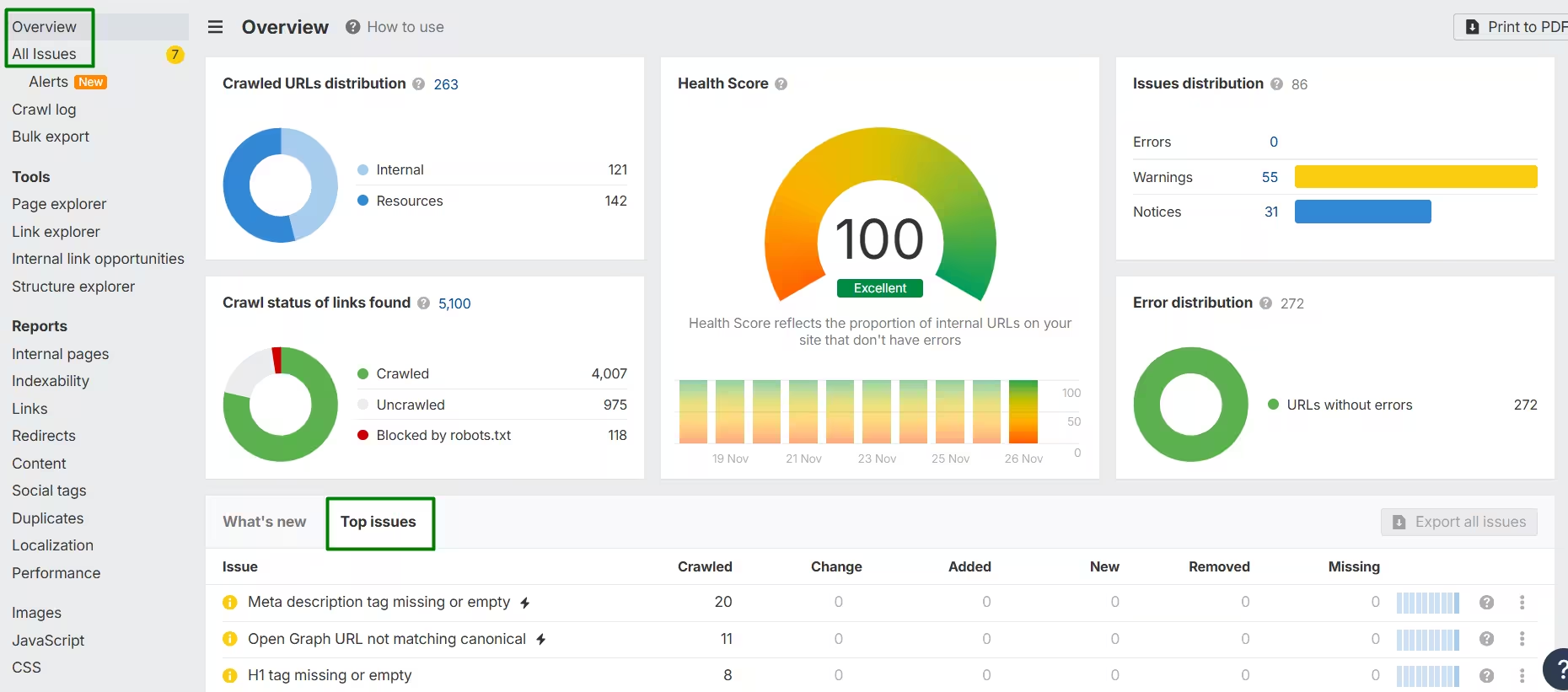
Here’s a quick idea of how you can use Ahrefs to identify your Google indexing issues.
After connecting your website to Ahrefs, click on the Health section in the dashboard. You’ll see the full overview, where you can explore the top issues and all detected errors. You can also identify the exact pages and locations where each issue is coming from.
If you need help connecting your project to Ahrefs, you can check their quick official guide on how to add project.
SECTION 03
How to Fix Google Indexing Issue Step by Step
To resolve indexing issues, first check if the affected page is disallowed in the robots.txt file or excluded using a noindex tag.
Fixing robots.txt and Noindex to Resolve Indexing Issues
A single wrong noindex or blocked by robots.txt can cause dozens of URL errors.
Fixing it clears all of them together.
Imagine you have an important page that you want indexed, but when you manually check your robots.txt file, you notice that the page is disallowed, as shown in the image.
For example:
1. Open your robots.txt file and
go to
https://yourwebsite.com/robots.txt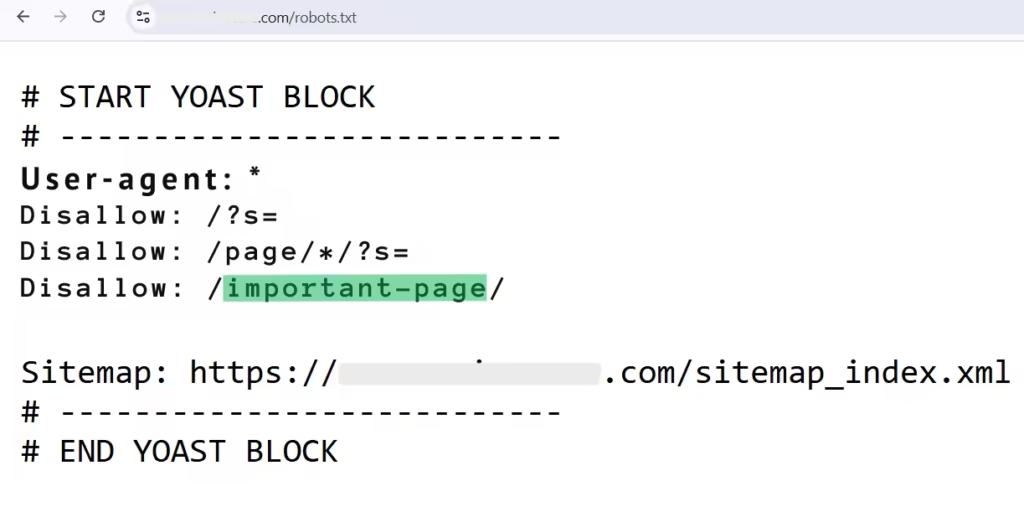
Now, go to the settings of the SEO plugin you’re using in your website dashboard, remove the disallow rule from the robots.txt file, and save the changes.
2. Look for lines like:
Disallow: /blog/
Disallow: /important-page/
Disallow: /category/how-to/
3. If the page you want indexed is listed under Disallow, remove that line.
Before fix:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /important-page/After:
User-agent: *
Allow: /important-page/If you’re using Yoast or Rank Math SEO, I’ve shared their official quick tutorial videos below so you can check them out.
1. Update robots.txt file in Yoast SEO plugin, and
2. How to edit robots.txt with Rank Math
Then, go to Google Search Console and submit the affected page under ‘Validate Fix’
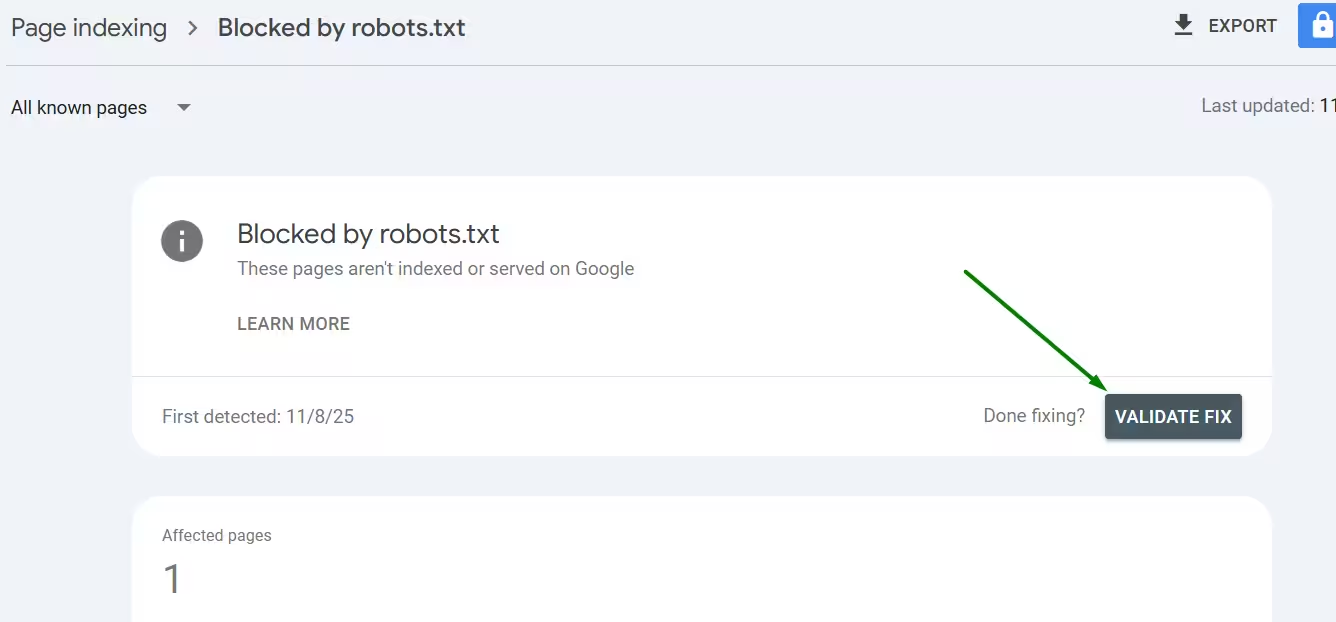
A wrongly applied noindex tag can instantly create a google indexing issue, even if the page is otherwise perfect.
Check for Noindex Tag
-
Open the affected page in your browser and check View Page Source.To find it quickly, open the affected page and press Ctrl + U.
-
Look for
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">or<meta name="googlebot" content="noindex">
If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, check your SEO plugin settings. I’ll show you how to do it using the Yoast SEO plugin.
First, go to the Edit option of the affected post. Then, scroll down to the Advanced section at the bottom. Find the setting labeled “Should search engines follow links on this content?” If it’s set to No, change it to Yes, as shown in the image.
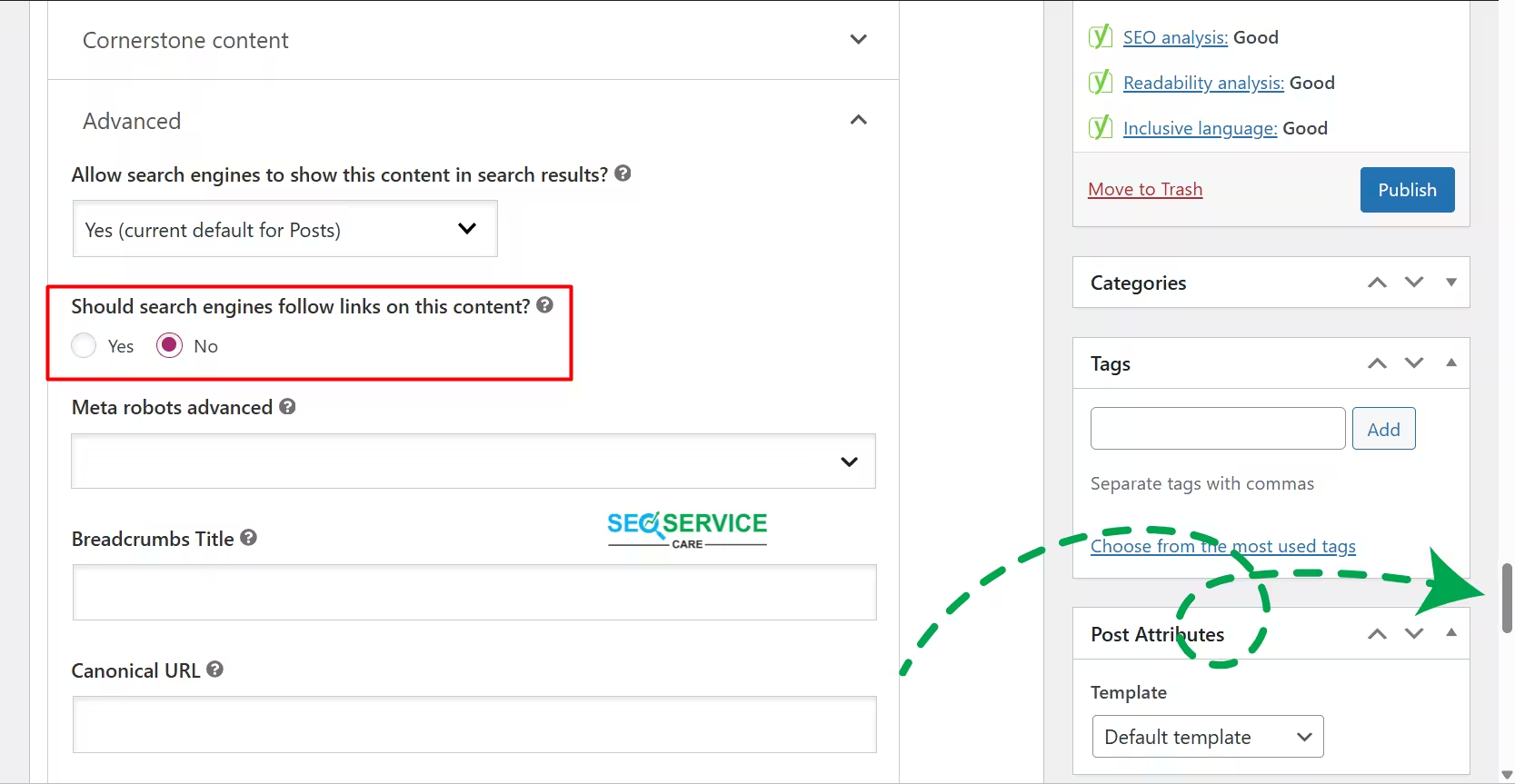
If you’re using Yoast or RankMath,
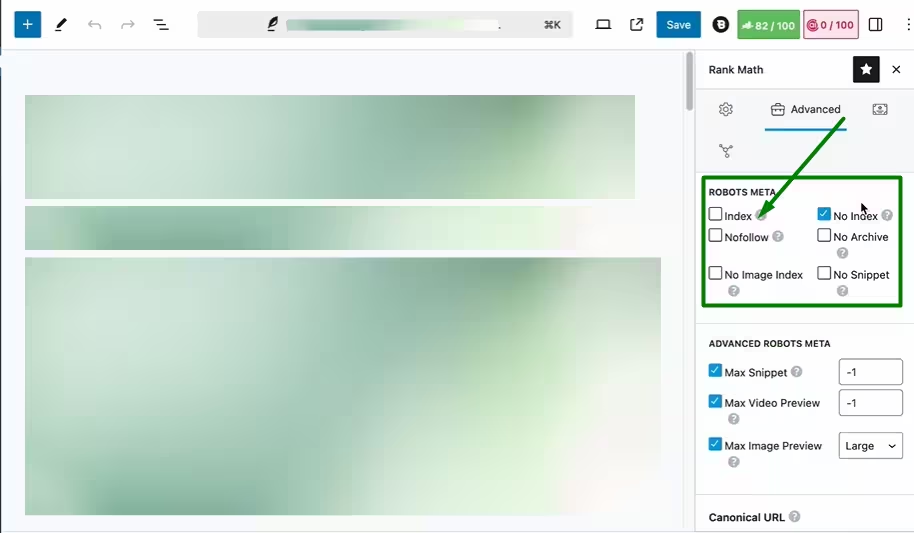
-
Open the Page Editor
Navigate to the page that is affected and open it in your editor. -
Check the Rank Math Tab
Click on the Rank Math tab. You’ll see if a noindex robots meta tag has been applied to the page. -
Access Advanced Settings
Switch to the Advanced tab within Rank Math to manage indexing settings. -
Set to Index
If the page is set to noindex, change it to index. This allows Google to crawl and display the page. -
Save Changes
Don’t forget to save your changes. Once saved, your page is ready for Google to re-crawl.
Align Both Settings
Make sure both the meta directives and the robots.txt rules are consistent.
If one allows indexing but the other blocks crawling, indexing will still fail.
Re-submit in Google Search Console
-
Open URL Inspection
-
Click “Request Indexing”
-
Google will know the page is ready to be indexed again
Note: Always use noindex carefully; only for low-value, duplicate, or temporary pages. Never block important pages, so Google can crawl and index them properly.
Strengthen Internal Linking
When internal linking is done incorrectly, Google may fail to recognize and prioritize your important pages.
[Several indexing issues in GSC, such as 404, Crawled but Not Indexed, or Discovered but Not Indexed, are often directly tied to weak internal linking. That’s why I’m highlighting the internal linking factor first, so the rest of the explanations make more sense.]
Common Internal Linking Mistakes
-
Not linking to new or important pages from other relevant pages
-
Linking from non-indexed or low-quality pages to high-value pages
-
Repeating the same anchor text too many times, looks like keyword stuffing
-
Keeping old internal links that point to removed or 404 pages
-
Broken links caused by http to https changes or slug mismatches.
These issues signal to Google that:
“This page is not very important.”
Result:
-
Lower crawl priority
-
Slow indexing
-
In some cases, the page may not get indexed at all
Internal Linking Best Practices
The purpose of internal linking is to help Google and users understand which pages on your site are most important.
Here’s how to do it effectively:
-
Link from pages that are already indexed and getting traffic
If a page is already indexed and performing well, link from that page to your new or important page.
This passes authority and helps Google recognize the new page faster. -
Use topic-relevant anchor text
Your anchor text should clearly describe what the linked page is about.
Examples:-
Headphone Buying Guide
-
Best Noise Cancelling Headphones 2025
-
-
Ensure each important page has at least 3–5 internal links
This helps Google understand the context and importance of the page. -
Focus on contextual internal links
Besides menu or footer links, make sure to link within the content itself (e.g., from body text, related articles, product comparison sections).
Google values contextual links more. -
Fix any broken or incorrect internal links
Double-check for:-
http→ should behttps -
Missing trailing slash / (if your site structure requires it)
-
Incorrect or outdated URL slugs
-
Old URLs still being referenced
-
Even these small errors can confuse Google’s crawlers and block proper indexing. When internal linking is done correctly, Google clearly understands:
“This page is important — crawl it and index it.”
Not Found (404)
From my experience auditing websites, broken or incorrect links are one of the main causes of indexing or 404 issues.
Check the Page Indexing section in Google Search Console to see all 404 errors. Then click on the affected URL to understand what caused the issue and why Google can’t find the page.
You can fix “not found” error in several ways:
1. Free way to fix not found error
I’ve already covered this topic in another article, which you can read to learn how to detect and easily fix 404 errors using Google Search Console and Ahrefs without spending a dime.
2. Paid Way to using Premium plugin
If you are using Yoast SEO Premium, this becomes very simple. From your website dashboard, go to Yoast, then Redirects, and follow the steps shown in the image.
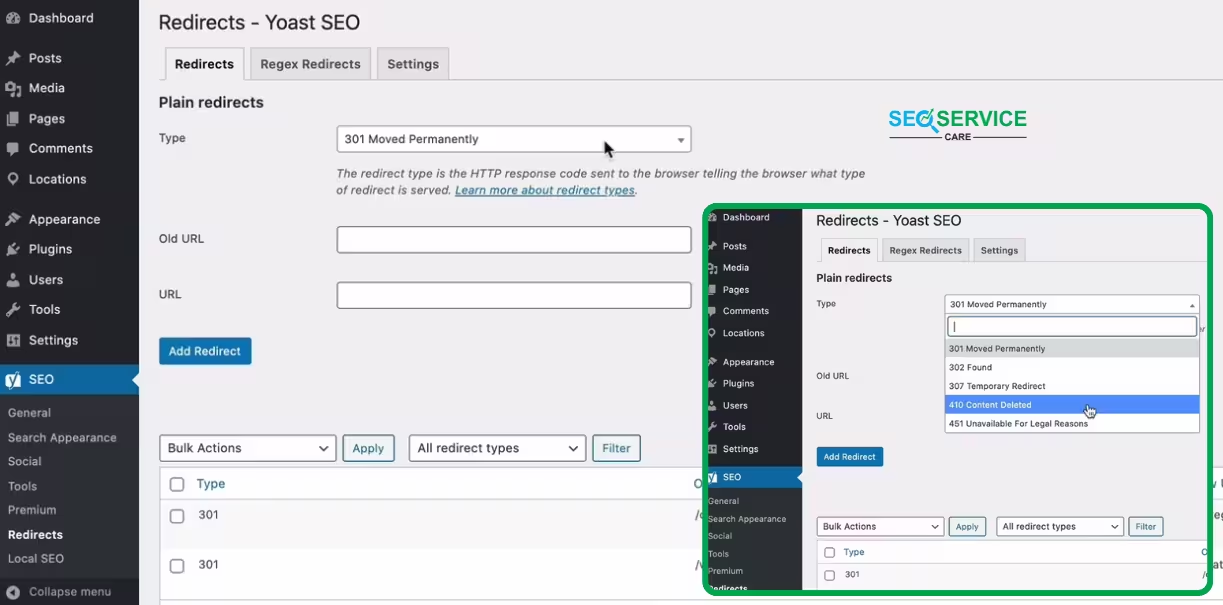
Note: If the page old URL is important and it receives traffic, then you should select the 301 “Moved Permanently” option. But if the URL is not necessary anymore and still flagged in Google Search Console, then choose 410 “Content Deleted.”
Enter the old URL into a dedicated plugin such as Ultimate 410 Gone Status Code or 410 Response Manager. The plugin returns a 410 status and signals to Google that the content is permanently gone. In that case, deleting the content from the old URL will not cause any issues.
Page with redirect
To fix “Page with redirect”, you first need to verify whether the redirect is correct.
If the redirect is intentional, then this is not an error. Google naturally will not index that URL, and this behavior is completely normal.
If the redirect is incorrect, then it must be fixed.
A redirect is considered wrong when:
-
it points to the wrong destination
-
it uses 302 or 307 instead of a 301
-
there is a redirect loop
-
there is a long redirect chain
-
the target URL is broken or returns a 404
Once these issues are corrected, Google will recrawl the URL, and it will be removed from the “Page with redirect” list.
Soft 404
Google shows a Soft 404 when a page is technically live but fails to provide sufficient value or information for users. In simple terms: “The page exists, but it does not serve any real purpose.”
How to fix it:
1. Improve the content
Create informative, helpful, and relevant content for users. If the content is thin or repetitive, Google may consider it low-quality and show a Soft 404.
2. Avoid incorrect redirects
Redirecting old or deleted pages directly to the homepage is not recommended. Instead, redirect only to closely related pages. If no relevant page exists, create new and useful content for that old URL.
This approach shows Google that you prioritize user experience rather than just trying to hide broken URLs.
I believe this isn’t a best practice rather, it’s a wrong one. John Mueller made this point very clear a long time ago. He mentioned this around the 4-minute-52 mark in the video.
In short: Always point duplicate or alternate versions to the correct canonical URL. Double-check that every canonical tag matches the page you want indexed. This helps Google understand your preferred content and maintain stronger SEO performance
Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
This status means Google is aware of your page (it has discovered it) but hasn’t crawled or indexed it yet. This usually happens when Google finds many pages on your site and, due to crawl budget limits, decides to delay crawling some of them.
To fix this, begin by strengthening internal linking (see Internal Linking Best Practices above, i have alreadydiscussed). This increases the page’s perceived importance in the site structure.
This helps Google understand that the page is part of your site’s structure and holds importance within your content network.
Next, evaluate and improve content depth. Quality content increases the likelihood of Google choosing to crawl and index it.
Finally, maintain a healthy crawl budget by removing or noindexing low-value or duplicate pages. When Google does not waste resources on unnecessary pages, it can focus on indexing your important content more efficiently.
Point to be noted: Google does not index every page by default. It indexes pages faster when they deliver strong internal relevance, clear value, and good technical performance. By strengthening these signals, you could significantly increase the chances of your page appearing in Google search results.
Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
This status means Google already crawled the page, but chose not to add it to the index yet.
In other words, Google saw the content, but didn’t find enough unique usefulness.
This issue closely matches ‘Discovered but Not Indexed’, but with one key difference: Google crawls the page and still chooses not to index it.
Most solutions are similar to the previous indexing issues, but here are some specific improvements to focus on for this case:
1. Add Unique, First-Hand Value
Google skips pages that feel generic or similar to others already indexed. Expand the content with helpful details, examples, FAQs, or visuals. Demonstrate real experience or expertise in the topic.
Improve the page by adding:
-
Real examples or case studies
-
Updated data or statistics
-
Unique comparison tables
-
Personal or professional insights
Example: Instead of just listing “10 SEO tips,” include real data or screenshots from your analytics results showing how those tips improved performance.
2. Strengthen Signals That the Page Matters
(Internal linking best practices already discussed earlier, apply them here.)
Additionally:
-
Ensure the page is included in your XML sitemap
-
Share the page on channels where engagement occurs. Example: When you share a page on social platforms, Google can discover it faster, which may help speed up crawling.
3. Trim Low-Value or Repetitive Sections
If a page contains filler or repeated paragraphs, Google may treat the entire page as low-value.
Remove anything that does not directly help the reader/visitor.
4. Check for Crawl Rendering Issues
Sometimes Google crawls the URL but cannot properly process the content.
Use:
Google Search Console > URL Inspection Tool
Check “Crawled Successfully?” and Rendered HTML preview.
If JS or server delay affects rendering, fix it accordingly.
Sitemap
A sitemap doesn’t guarantee page indexing, but it shows Google which pages are most important and how to crawl them.
Common Sitemap Problems
-
Outdated URLs: Pages that no longer exist or return 404 errors.
-
Non-Canonical URLs: URLs that point to other canonical pages.
-
Blocked URLs: Pages blocked by
robots.txtornoindextags. -
Incorrect XML Format: Missing
<loc>tags or structural errors. -
Oversized Sitemap: More than 50,000 URLs or over 50 MB in size.
How to Fix Sitemap Issues
- Validate Your Sitemap
Go to GSC dashboard > Sitemaps and check for any “Couldn’t fetch” or “Error” messages.
You can also validate it using an external tool like XML Sitemap Validator. - Remove Broken or Invalid URLs
Keep only live (200-status) URLs in your sitemap. - Include Only Indexable URLs
- Enable Auto-Update for Your Sitemap
If you’re using WordPress, make sure your SEO plugin (like Yoast SEO or RankMath) automatically updates the sitemap whenever you publish or delete a post.
Example:https://yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml - Resubmit the Sitemap in Google Search Console
Once updated, go to Search Console > Sitemaps and resubmit it.
Check the “Last read” date. If it’s recent, Google has successfully re-crawled your sitemap.
In GSC’s Pages report, verify that the URLs listed in your sitemap are actually being indexed.
My suggestion:
For large websites, it’s best to split sitemaps by type, for example:
-
/blog-sitemap.xml -
/product-sitemap.xml
This improves crawl efficiency and ensures your most valuable pages get indexed faster.
5xx Server Errors
Google Search Central clearly states that server errors directly block crawling and affect a page’s indexability.
First, you need to log in to your hosting provider’s dashboard. Most hosting services, like cPanel, Plesk, or other custom control panels, have a section called Metrics or Logs. There, you can find the Error Logs option.
Each entry in the Error Logs will show which page or file encountered a problem during crawling. For example, if you’re getting a 500 Internal Server Error while loading https://mywebsite.com/blog-post, the log will indicate which file or line caused the fatal error. For instance, it might say: single.php line 120: Fatal error.
This means a fatal error occurred on line 120 of the single.php file. It indicates that there’s an issue with the theme’s code or a plugin.
After that, you can fix the file or the specific piece of code. Start by taking a backup of the file. Then identify which function or variable is causing the issue on that line. For example, if the code contains:
echo get_post_meta($post->ID, 'headphons', true);
There is a typo here. Instead of headphons, it should be headphones. Correcting the typo would resolve the error. In the same way, you may need to replace deprecated functions or update or deactivate a plugin if it is causing the problem.
If a 502 Bad Gateway error appears and the issue resolves after deactivating a specific plugin (such as “SEO Plugin X”), it indicates a plugin conflict. Updating or reinstalling the plugin typically fixes the issue and restores normal page loading.
In the case of 503 or 504 errors, the issue is usually related to server resources. Increasing the server’s RAM or CPU, restarting the server, or contacting your hosting provider can help resolve it. Misconfigured CDN or firewall settings can also trigger 503/504 errors. For example, if you’re using Cloudflare, you may need to adjust the Page Rules to increase the timeout limit or perform a cache purge.
Once you fix everything, use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to check the page and request indexing. This notifies Google that you have made the page ready for indexing.
Expert Tip: 5xx errors not only affect indexing but also impact user experience. Consistently monitoring your server, hosting, theme, plugins, and CDN is crucial for maintaining good SEO. After resolving these issues, the page re-enters Google’s crawl and indexing process, helping restore indexing and improve overall SEO performance.
JavaScript Rendering Issues
Modern websites often rely heavily on JavaScript to display dynamic content such as product details, reviews, or interactive sections. However, if Googlebot cannot properly render your JavaScript, it may miss those sections, preventing Google from indexing them.
Now, how to Fix JavaScript Rendering Problems?
Implement Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or Dynamic Rendering
Instead of relying on the browser, render your page content on the server and deliver a complete HTML version to Google.
Frameworks like Next.js, Nuxt.js, and Angular Universal support this by default.
Example:
If your product details appear only after clicking a “View Details” button, SSR includes that information in the HTML before Google crawls it.
Ensure Important Content Loads Without User Interaction
Google doesn’t click buttons or scroll infinitely.
Make sure key content such as headings, text, and links appears immediately during the initial load.
Avoid Delayed or Conditional Rendering
Scripts that load after a delay or depend on third-party resources may time out before Google finishes rendering.
Keep essential scripts lightweight and prioritized early in the load process.
Test Again Using the URL Inspection Tool
After making changes, re-check the rendered version in Google Search Console and click Request Indexing.
If the rendered HTML now matches what users see, the problem is resolved.
Optimize JavaScript and CSS Delivery
Minify and combine files, and defer non-critical scripts.
This not only improves rendering and crawlability but also enhances page speed and user experience.
Take note of this: Googlebot uses the Web Rendering Service (WRS). Which sometimes delays JavaScript rendering for several days.
That’s why pre-rendering or SSR is the most reliable way to ensure your content is visible to Google immediately. That will improving both crawl efficiency and indexing speed.
FAQ’s about Google Indexing Issue
Q.1: How to fix page is blocked from indexing?
Check for robots.txt rules, meta noindex tags, or other restrictions and remove them to allow Google to index the page.
Q.2: What do page indexing issues mean?
Page indexing issues happen when Google hasn’t added your page to its search results yet. This can occur if the page is new, missing from your sitemap, or if Google hasn’t found a link to it. Even after requesting a crawl, it can take a few days to weeks for new pages to appear in search results.
Q.3: Can I pay Google to rank my website higher?
No, you cannot pay Google to improve your organic search rankings. Google ranks pages based on relevance, quality, and user experience, not payment. Paid ads, like Google Ads, are separate from organic search results.
Q.4: How long does it take to fix a google indexing issue
There is no fixed timeline. Some sites recover from a google indexing issue within hours, while others take weeks.
Closing Remarks
Google indexing problem is common but fixable. By carefully checking for noindex tags, robots.txt blocks, canonical errors, broken links, and content quality, you can guide Google to properly crawl and index your pages. Combine this with strong internal linking, optimized sitemaps, and error-free server setup to improve your site’s visibility.
Regularly reviewing your setup ensures your pages overcome indexing issues and stay visible to users.